|
|
|
 |
The Bible
Mentions Asnapper (Ashurbanipal).
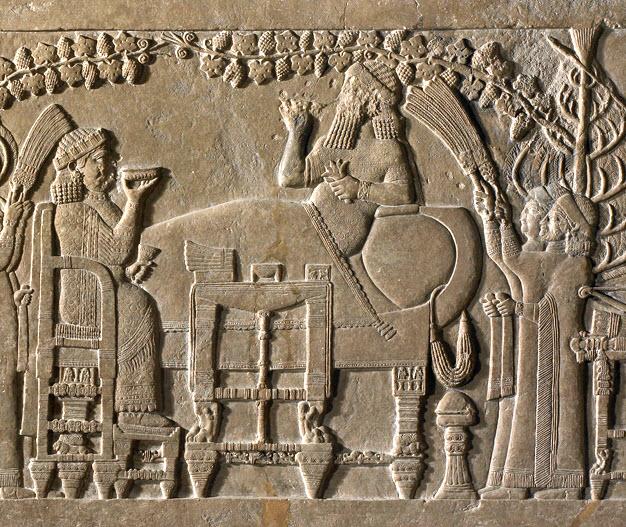
This miniature relief shows Asnapper feasting with his queen in
his royal garden enjoying the spoils of war. Little did they
know that the Assyrian Empire was soon to fall. The Bible mentions
king Asnapper in Ezra 4:10 |
This miniature replica is of Ashurbanipal,
King of Assyria, feasting in his royal garden with his queen. The
bas-relief is from his palace at his ancient capital, Nineveh. His
Biblical name was Asnapper. The panel was discovered at the site of ancient
Nineveh during the reign of Ashurbanipal (668-626 BC). The original is
located at the British Museum in London. The alabaster relief is part of
a panel standing over 25 inches tall.
Ezra 4:10 - and the rest
of the nations whom the great and noble Asnapper brought
over, and set in the city of Samaria, and in the rest of the country
beyond the River, and so forth, wrote.

This map shows the primary capitals of the Neo-Assyrian Empire
Museum Images

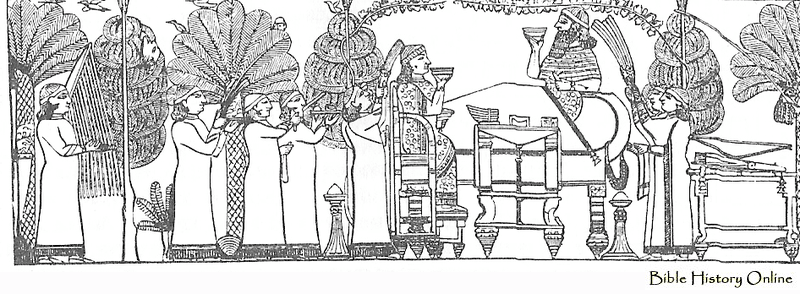

Information about the Ashurbanipal
Feasting Relief
- Limestone relief from the N. palace of
Ashurbanipal at Nineveh, his capital.
- Ashurbanipal reigned from 668-626 BC.
- Ashurbanipal was the grandson of Sennacherib and son of Esarhaddon
- The detailed relief is 139 cm (4 1/2 feet) wide.
- The relief reveals the king and queen feasting in his royal garden
- They are on their thrones and the king is reclining and at rest
- He is relaxed and has laid aside his weapons, sword, bows and arrows
- They are sipping libations from bowls and being fanned by attendants
- The garden is filled with grape vines, conifer and palm trees lined
with birds
- His wife Ashursharrat in a richly
decorated robe is seated on an elegant throne with a footstool.
- The head of the Elamite king (Te-umman)* is
hanging on the tree on the left
- From the Neo-Assyrian Period (1000-612 BC).
- Excavated at the site of ancient Nineveh (Kuyunjik) by H. Rassam about
1847.
- This stone panel is currently at the British Museum in London.
- Nineveh (Kuyunjik) was Ashurbanipal's capital city (Northern Iraq).
- Ashurbanipal was one of the most energetic and cruel of the Assyrian
kings
- Ashur-bani-pal was the last of the great Assyrian kings
As one scholar eloquently puts it, "The Bible mentions "the great and noble
Asnappar" who is actually Ashurbanipal, the son of Esarhaddon, who
succeeded his father on the throne and reigned from 669-626 BC. He was
the last of the great Assyrian kings. This relief scene was carved on
alabaster and depicts the king of Assyria, Ashurbanipal, reclining on a
well upholstered couch. He is in the royal park, which is planted with
date palms, conifers and shrubs. Vine tendrils, leaves and grapes, shade
the king. He is relaxed and has laid aside his weapons, sword, bows and
arrows. He is wearing a headband with streamers and an embroidered
coverlet with tassels at the corners is spread over his legs. With his
right hand he raises a goblet to his lips, in his left hand he holds a
flower. Beside the couch is a table laid with food. Opposite him is his
wife Ashursharrat in a richly decorated robe sitting on an elegant
throne with a footstool. She is also drinking. Servants bring them food
and other servants wave fly-whisks. In the background a musician plays a
lyre with 11 strings. Not such a peaceful scene because off in the left
corner a head is hanging from a tree. This head might be the king of
Elam because this scene Ashurbanipal is celebrating his victory over the
Elamites at the battle of Susa in 655 BC."
Asshurbanipal and his wife in a vine bower.
668-626 BC.
"There [is] Elam and all her multitude round about her
grave, all of them slain, fallen by the sword, which are gone down
uncircumcised into the nether parts of the earth, which caused their
terror in the land of the living; yet have they borne their shame with
them that go down to the pit." - Ezekiel 32:24
"And the rest of the nations whom the great and noble Asnappar
brought over, and set in the cities of Samaria, and the rest [that are]
on this side the river, and at such a time." - Ezra 4:10
*based on their recent victory over the
Elamites at the Battle of the River Ulai, or of Til-Tuba.
Some translations of the inscriptions
on Ashurbanipal's sculptures reads:
One inscription on a sculpture of
Te-umman and Tamritu his first-born son being slain by Assyrian soldiers
reads: "Te-umman, king of Elam, was wounded in fierce battle, and his
eldest son Tamritu took him by the hand, and to save their lives they
fled and hid themselves in a wood. With the help of the gods Ashur and
Ishtar I [Ashur-bani-pal] seized them and I cut off their heads in the
presence of each other."
Another inscription on a sculpture of soldiers in a chariot who are
carrying Te-umman's head to Assyria reads: "The head of Te-umman, king
of Elam, which they had cut off in the battle in the sight of mine army
as a symbol of glad tidings they carried quickly to Assyria."

Museum Excerpt
Museum number ME 124920
Ashurbanipal and his Queen enjoying a
banquet
This panel was the focal point of a decorative scheme incorporating all
the triumphs in war and sport of which King Ashurbanipal (reigned
669-631 BC) was most proud. The panel probably decorated one of the
King's private apartments, as the carving of the scene is exceptionally
fine.
The queen sits facing Ashurbanipal. Queens, like women in general, were
seldom represented in Assyrian sculpture. However, women did sometimes
hold power at the Assyrian court, though usually behind the scenes.
Documents suggest that Ashurbanipal's grandmother, Naqia-Zakutu, was
extremely influential in promoting her son Esarhaddon and then
Ashurbanipal to the throne.
The scene also shows a harpist. Images of musicians are among the most
important sources for understanding ancient musical instruments. The
details in the carving appear to be very accurate.
On the tree in front of the harpist is a human head, that once belonged
to Teumman, king of Elam, who had fought against Assyria. Consequently
Ashurbanipal's army invaded Elam. The campaign was illustrated as
redecoration in one of the rooms of the palace of his grandfather
Sennacherib (reigned 704-681 BC).
The mutilation of the faces of the king and queen was probably done by
an enemy soldier when the Median and Babylonian armies ransacked Nineveh
in 612 BC.
Dimensions
Length: 58.420 cm
Width: 139.700 cm
Depth: 15.240 cm
The palace was excavated by H. Rassam
(from 1853)
British Museum Page
 The Assyrian
Empire The Assyrian
Empire
The first great military empire in ancient history
was the Assyrian Empire. By the time of Ashurnasirpal and Shalmaneser
III in the 9th century BC the Assyrians organized a mighty army of
nearly 200,000 soldiers. Their military strategy was unsurpassed up to
that time, and with the age of iron they were an unstoppable fighting
machine. They brought spearmen, archers, shieldmen, slingers, siege
engines, chariots, and a huge calvary into the battlefield. The mighty
Assyrians dominated the ancient world until they were crippled by the
God of Israel in the reign of Sennacherib. God raised up the Assyrians
to remove Israel out of his sight for their rebellion and idolatry, but
the Assyrians would also be punished also for their wicked ways. They
finally fell to the Medes and Babylonians in 612 BC and passed into
history.
 Assyrian Kings Mentioned in the Bible
Assyrian Kings Mentioned in the Bible
2 Kings 15:29 -
In the days of Pekah king of Israel, Tiglath
Pileser king
of Assyria came and took Ijon, Abel Beth Maacah, Janoah, Kedesh, Hazor,
Gilead, and Galilee, all the land of Naphtali; and he carried them
captive to Assyria.
2 Kings 15:19 - Pul the
king of Assyria came against the land, and Menahem gave Pul one thousand
talents of silver, that his hand might be with him to confirm the
kingdom in his hand.
2 Kings 18:9 -
And it came to pass in the fourth year of king Hezekiah, which [was] the
seventh year of Hoshea son of Elah king of Israel, that Shalmaneser king
of Assyria came up against Samaria, and besieged it.
Isaiah 20:1 -
In the year that Tartan came unto Ashdod, when Sargon the
king of Assyria sent him,) and fought against Ashdod, and took it;
2 Kings 19:16 -
LORD, bow down thine ear, and hear: open, LORD, thine eyes, and see: and
hear the words of Sennacherib,
which hath sent him to reproach the living God.
2 Kings 19:37 -
And it came to pass, as he was worshipping in the house of Nisroch his
god, that Adrammelech and Sharezer his sons smote him with the sword:
and they escaped into the land of Armenia. And Esarhaddon his
son reigned in his stead.
Ezra 4:10 - and the rest
of the nations whom the great and noble Asnapper brought
over, and set in the city of Samaria, and in the rest of the country
beyond the River, and so forth, wrote.
Assyrian Kings Names in Cuneiform
Archaeology
of Ancient Assyria
Timeline of Ancient Assyrian Kings
(During the Period of the Biblical Kings)
Assur-nasirpal II (885-860
B.C.) A cruel warrior king, he made Assyria into the most fierce
fighting machine of ancient world.
Shalmaneser III (860-825
B.C.) His reign was marked by almost constant war. He was the first
Assyrian king to come into conflict with Israel. King Ahab fought
against him, and king Jehu paid him tribute in 841 BC. His royal
inscriptions were more detailed and more numerous than any other king.
His building works were massive just like his father Assurnasirpal II.
See Shalmaneser
and the Black Obelisk.
Shamsi-Adad V (825-808
B.C.) Most of his reign was focused on Babylonia and his own internal
conflicts.
Adad-nirari III (808-783
B.C.) The little information about his reign mentions his building
projects at Calah and Nineveh, as well as a conflict at Der in Babylonia
and collecting tribute in Damascus, Syria.
Shalmaneser IV (783-771
B.C.) The limited knowledge of his reign reveal some conflicts in
Damascus and a period of decline in Assyria.
Assur-dayan III (771-753
B.C.) The little information about this ruler reveals Assyria being in a
period of decline.
Assur-nirari V (753-747
B.C.) There is very little information about his reign. The king of
Urartu boasted of a victory over this king of Assyria in an inscription.
Tiglath-pileser III (Pul)
(747-727 B.C.) He restored Assyria to a major world power. He is the "Pul"
mentioned in the Bible and the one who began to destroy Samaria, the
capital of the Northern Kingdom of Israel. He carried many away into
captivity. This captivity is mentioned in his own inscriptions, the
Babylonian Chronicle, and the Bible.
Shalmaneser V (727-722
B.C.) He besieged Samaria, the capital of the Northern Kingdom of
Israel. He died during the siege after imposing taxation on the holy
city (Asshur), and his son Sargon came to power.
Sargon II (722-705
B.C.) He completed the destruction of Samaria and the captivity of
Israel. He was also famous for his magnificent palace with his colossal
winged guardians.
Sennacherib (705-681
B.C.) He was the most famous of the Assyrian kings. He mentions the name
of Hezekiah on his prism during his war campaigns, he claimed to have
"Hezekiah captured in his own royal city (Jerusalem) like a caged bird."
His army was defeated at the gates of Jerusalem by the Angel of the
Lord. Sennacherib returned back to Nineveh and was killed violently by
his own son, as mentioned in the Babylonian Chronicle, The Bible, and
various other inscriptions. He also conquered Babylon.
Esar-haddon (681-668
B.C.) He rebuilt Babylon, invaded and conquered Egypt by crossing over
the Sinai Desert with Arab camels carrying water for his army, and was
one of Assyria's greatest kings. He died fighting Egypt.
Assur-banipal (668-626
B.C.) He destroyed the Thebes in Egypt and collected a great library,
innumerable clay tablets were found.
Assur-etil-ilani (626-607
B.C.) It was under his reign that the Assyrian Empire fell.
 Assyrian
annals mention contacts with some ten Hebrew kings: Omri, Ahab, Jehu,
Menahem, Hoshea, Pekah, Uzziah, Ahaz, Hezekiah, and Manasseh. Assyrian
annals mention contacts with some ten Hebrew kings: Omri, Ahab, Jehu,
Menahem, Hoshea, Pekah, Uzziah, Ahaz, Hezekiah, and Manasseh.
In the reign of Hoshea, king of Israel, Shalmaneser, king of
Assyria, twice invaded (2 Kings 17:3,5) the kingdom that remained, and
his successor Sargon II took Samaria in 722 BC, carrying away 27,290 of
the population as he tells in his Khorsabad Annals. Later Assyrian
kings, particularly Esarhaddon (681 BC - 668 BC), completed the task.
For More Info See:
Bible History Online
Map of the Land of Assyria

Kids Bible Maps
Primary Sources for Assyrian History
The Assyrian Annals. The scribes of the chief cities of the
Assyrians wrote the accounts of the king's military campaigns on
cuneiform tablets, and clay prisms or cylinders. The accounts are very
reliable, even though the accounts do not speak negatively of the
Assyrians and are meant to glorify the king. The annals also give much
detail to geography and Chronology. It is interesting how accurate the
Assyrians were with dates, they made use of an Assyrian Kings List or
the Eponym Canon.
The Assyrian Chronicles and Eponym Canon. The Assyrian scribes
organized their national events whether military, political or religious
every regnal year. The Babylonian Chronicles were structured the same
way. Assyrian records were kept very carefully, they took their dating
and their history seriously. They attached their record of events with
the solar year and with the name of an official who was known as the "limmu."
Their was a new limmu appointed every year. They recorded military,
political and religious events in every year and made references to
eclipses. The Assyrian records are highly dependable and allow Biblical
scholars a very accurate way of dating events and designating "eponyms"
for 244 year in Hebrew history, from 892-648 BC.
The Assyrian King List.
The Assyrian King List reveals a list of the kings of ancient
Assyria in chronological order, from the 2nd millennium BC to 609 BC. It
lists the name of the king, his father's name, the length of his reign,
and some great achievements.
Assyrian Sculptures. The limestone bas-reliefs discovered
from the palace walls of major Assyrian capital cities like Nineveh (Kuyunjik),
Nimrud (Calah), Khorsabad (Dur-Sharrukin), and the bronze bands on the
Balawat Gates reveal a wealth of history. The illustrative events were
carved be professional Assyrian artists like a modern day photographer
on the scene. The carvings reveal the military might and tactics of the
Assyrians, as well as the futility of those nations that defied their
might. These sculptures are on display in museums around the world, for
example: The British Museum in London, The Louvre in France, The Iraqi
Museum, and The Oriental Institute in Chicago.
The Bible. The Old Testament records the history of the Kingdoms
of Israel and Judah, along with the battles of other nations. It
includes the fall of the 10 tribes in northern kingdom of Israel in 722
BC by the Assyrians, as well as the
fall of the southern kingdom of Judah in 586 BC by Nebuchadnezzar of
Babylon. The Bible also records miraculous events surrounding people
like Elijah, and Jonah, as well as the slaying of 185,000 Assyrians at
Jerusalem by the Angel of the LORD. The events recorded in 2 Kings
generally agree with Assyrian and Babylonian sources. |







